Effective Reporting in SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC)
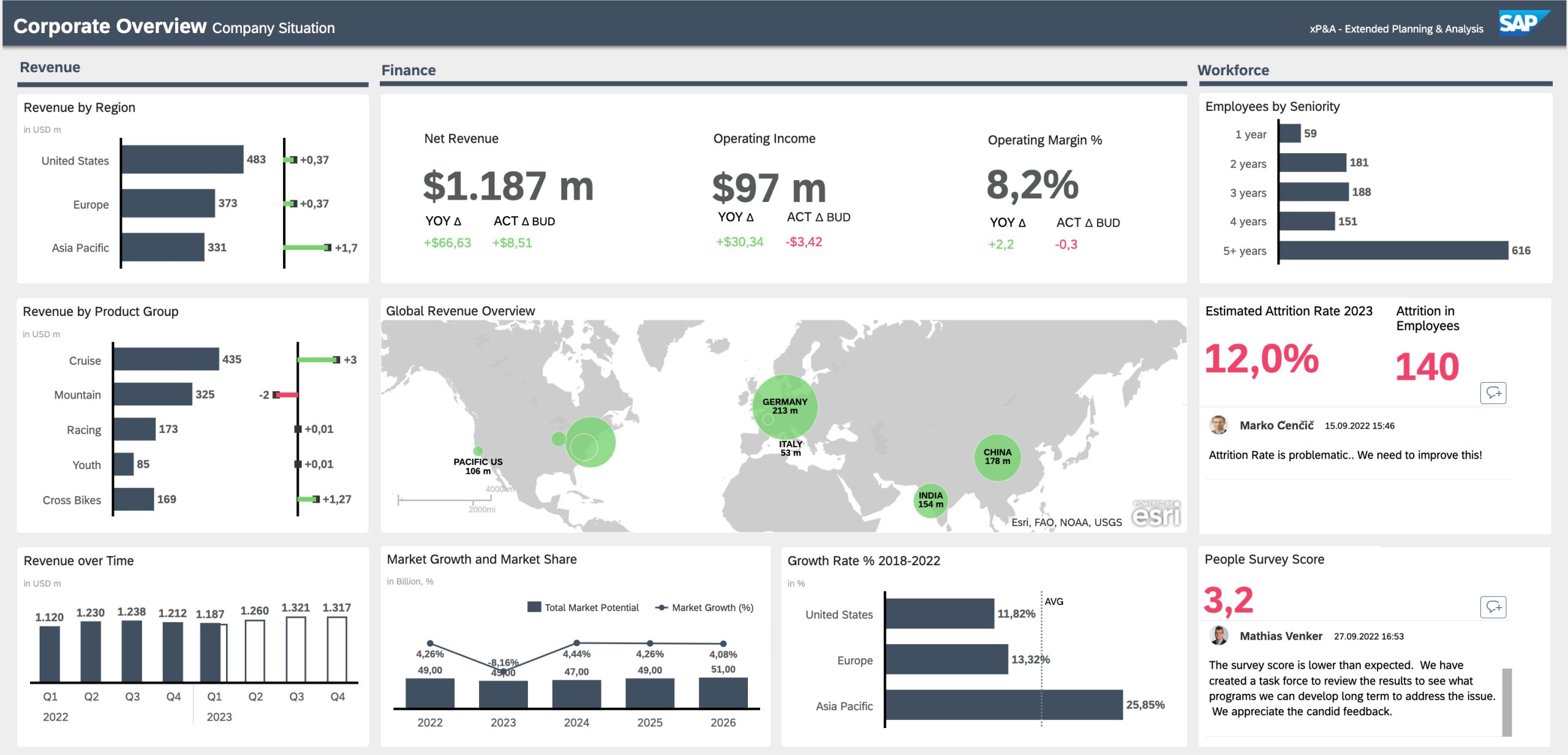
SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) is a next-generation SaaS-based solution from SAP that combines Business Intelligence (BI), planning, predictive analytics, and augmented analytics in a single platform. Built natively on SAP BTP (Business Technology Platform), SAC empowers users across departments to gain real-time insights, build interactive dashboards, and support strategic decision-making with reliable data visualizations.
In this post, we’ll focus specifically on reporting in SAP SAC—covering features, best practices, and the value it brings to finance and business professionals aiming to deliver meaningful, data-driven reports for stakeholders.
What is SAP SAC?
SAP Analytics Cloud integrates key analytical capabilities such as:
- Business Intelligence (BI)
- Planning and Budgeting
- Predictive Analytics
- Augmented Analytics (smart insights, natural language query)
- Collaboration tools
For reporting purposes, SAP SAC acts as a powerful visualization engine that consolidates data from various sources (SAP and non-SAP) and enables users to create dynamic, interactive reports and dashboards that respond to real-time business questions.
Why Choose SAC for Reporting?
Modern enterprises need agile, cloud-based reporting tools that offer:
- Real-time connectivity to live data
- Self-service analytics
- Mobile access
- Secure data governance
SAC checks all these boxes, especially when integrated with SAP S/4HANA, BW/4HANA, and other data sources. Its drag-and-drop interface, combined with intelligent features like Smart Insights and Smart Discovery, enables business users—not just IT teams—to create compelling reports independently.
Key Features of Reporting in SAP SAC
1. Story-Based Reporting
In SAC, reports are structured as stories—a storytelling paradigm that combines charts, tables, maps, and images in a logical narrative. Each story can contain multiple pages and visual elements such as:
- Bar/line/pie charts
- Cross tabs
- Geo maps
- Input controls
- Filters and drill-downs
This makes it easy to tell a complete story from your data—ideal for management reporting, board presentations, and business reviews.
2. Live vs. Imported Data
SAP SAC supports two main data acquisition modes:
- Live Connections: Connects directly to systems like SAP S/4HANA or SAP BW without storing the data in SAC.
- Import Connections: Brings data into SAC’s in-memory engine for further manipulation and modeling.
For real-time reporting, live connections are preferred. For more advanced calculations or planning, imported models provide additional flexibility.
3. Smart Features
SAC’s augmented analytics make it stand out in the reporting space:
- Smart Insights: Automatically explains variances in your data.
- Search to Insight: Natural language query functionality that lets users type questions like “Total revenue by region” and get instant visual answers.
- Smart Discovery: Helps uncover hidden patterns and relationships using machine learning.
These features allow users to generate insightful reports without deep statistical or technical knowledge.
4. Advanced Visualizations and Widgets
SAC offers a wide variety of visualization types that can be customized in terms of color, format, and interactivity. Widgets like KPI tiles, gauges, and tables support responsive layouts and drilldowns, helping users interact with data dynamically.
Advanced scripting using SAP Analytics Designer allows power users to create application-style dashboards for more controlled, guided analytics experiences.
5. Data Blending and Modeling
Users can blend data from multiple sources into one model for unified reporting. The Modeler in SAC supports calculated dimensions, measures, and hierarchies that enhance the reporting structure. It’s especially useful for scenarios like:
- Combining actuals from SAP S/4HANA with forecasts from Excel
- Merging data from different geographies or subsidiaries
Finance professionals benefit greatly by consolidating planning, forecasting, and actuals into a single, reconciled report.
Common Use Cases in Finance
1. Financial Statements and P&L Reporting
SAC enables automated generation of P&L, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow statements, pulling data directly from SAP ERP systems. Reports can be filtered by cost centers, departments, or time periods and can be enhanced with variance analysis (actual vs. plan vs. forecast).
2. Budget vs. Actuals Analysis
With integrated planning features, SAC is ideal for analyzing how budgets and forecasts align with actuals. Reports can be broken down by line items and provide automated variance highlights using conditional formatting.
3. KPI Dashboards for CFOs
Executives often need high-level overviews. SAC allows for customizable KPI dashboards showing metrics like:
- Revenue growth
- EBITDA margin
- Operating expenses
- Net working capital
These dashboards are interactive, allowing drilldowns for deeper investigation when necessary.
4. Audit and Compliance Reporting
Using filters, bookmarks, and comment features, finance teams can generate reports that align with audit trail and compliance needs. SAC’s tight security model also ensures sensitive data is protected with role-based access control.
Integration with Other SAP Systems
SAP SAC integrates seamlessly with:
- SAP S/4HANA: Real-time reporting on transactional data.
- SAP BW/4HANA: Leverages pre-built queries and InfoProviders.
- SAP Data Warehouse Cloud: Combines structured data across hybrid environments.
- SAP BPC: For planning and consolidation.
These integrations reduce duplication of work and ensure data accuracy across reports.
Best Practices for Reporting in SAC
1. Use Models Wisely
Structure your data models with clear naming conventions, dimensions, and hierarchies. Pre-calculate frequently used KPIs to improve performance.
2. Design for the Audience
Tailor stories to different user groups (e.g., executives vs. controllers). Use simplified visualizations for leadership, and detailed tables for analysts.
3. Apply Filters and Input Controls
Make reports interactive by adding filters, dropdowns, and sliders. This allows users to self-serve and explore data without needing multiple versions of the report.
4. Leverage Templates
Use standard templates for reports across departments to maintain consistency in layout, branding, and KPIs.
5. Enable Commenting and Collaboration
Encourage collaboration by enabling comments and discussions directly within stories. This makes SAC a true collaborative reporting tool.
Training and Skill Development
To master reporting in SAP SAC, finance professionals can:
- Take free openSAP courses like SAP Analytics Cloud for Business Users
- Explore tutorials and documentation on the SAP Help Portal
- Use SAP Learning Hub for in-depth certifications
- Practice building models and stories in demo or trial environments
Skills in data modeling, visual storytelling, and understanding SAC scripting (for advanced dashboards) are particularly useful.
Future of Reporting with SAP SAC
SAP continues to enhance SAC with AI-driven capabilities and tighter integration with Microsoft Office and Excel. Future enhancements may include:
- Improved predictive capabilities for forecasts
- Enhanced Excel add-ins for reporting flexibility
- Advanced planning integration using SAC’s Extended Planning and Analysis (xP&A)
Organizations that adopt SAC as their core reporting tool will benefit from faster insights, agile decision-making, and reduced IT dependency.
Conclusion
Reporting in SAP Analytics Cloud is more than just visualizing data—it’s about transforming data into a strategic asset. With its intuitive interface, smart features, and real-time connectivity, SAC enables finance and business professionals to deliver compelling, actionable reports that drive performance and support agile decision-making.
Whether you’re analyzing financial performance, building interactive dashboards for executives, or preparing variance reports, SAC empowers you to do it all within a secure, integrated, and intelligent platform.
Start exploring SAP SAC today and take your reporting to the next level.