Using FDWF for Financial Reports
In today’s enterprise finance landscape, data is everything—but having the right tools to analyze and report that data is just as critical. This is where FDWF (Financial Data Warehouse Framework) comes in. For SAP users and large finance teams, FDWF provides a unified, structured approach to managing and reporting financial data across multiple systems.
In this blog post, we’ll break down what FDWF is, how it works, and how you can use it to create efficient and insightful financial reports.
What is FDWF?
FDWF (Financial Data Warehouse Framework) is a modular and extendable data framework, typically used in conjunction with SAP systems, to facilitate financial reporting and data consolidation across multiple source systems.
FDWF acts as a centralized data model that harmonizes finance-relevant information, making it easier to create reports, analyze trends, and ensure data accuracy across business units.
Core objectives of FDWF:
- Enable end-to-end data traceability
- Support multi-dimensional reporting
- Provide a standardized financial data model
- Enable compliance-ready financial statements
Why Use FDWF for Financial Reporting?
Financial reporting isn’t just about balance sheets or income statements. Organizations need to:
- Combine financial and operational data
- Consolidate figures across business units and geographies
- Ensure data governance and auditability
- Generate real-time, interactive reports for decision-making
FDWF solves these needs by providing a consistent layer between raw transactional systems (like SAP S/4HANA or ECC) and reporting layers (like SAP Analytics Cloud or BI platforms).
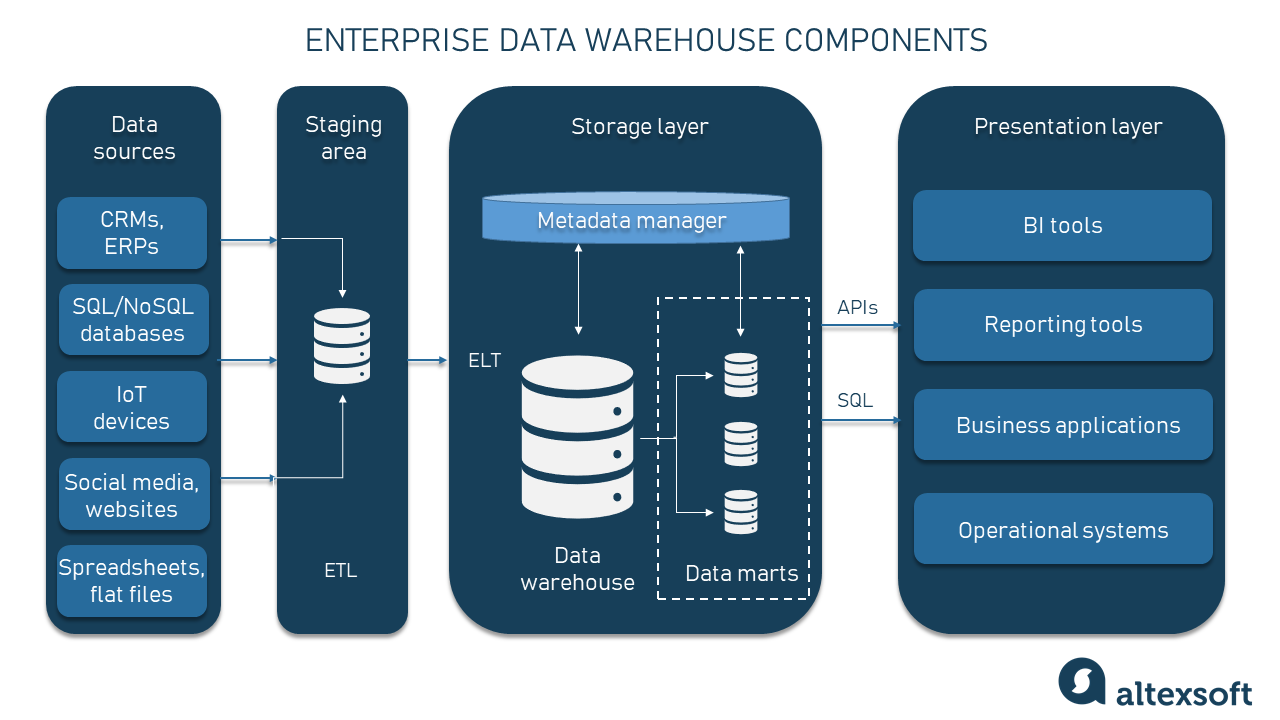
Key Components of FDWF
Let’s look at the components that make FDWF a powerful reporting framework:
1. Data Acquisition Layer
- Pulls data from source systems (SAP, non-SAP, third-party)
- Supports scheduled extractions and delta loads
2. Data Harmonization Layer
- Applies mapping logic, currency conversion, and data quality checks
- Aligns different Chart of Accounts or fiscal periods
3. Data Warehouse Layer
- Stores structured data models: Trial Balance, P&L, Balance Sheet
- Enables slice-and-dice by entity, region, department, or cost center
4. Virtual Data Models (VDMs)
- Predefined views for reporting
- Supports SAP CDS Views or SQL-based models for BI tools
5. Reporting Layer
- Integrates with SAP Analytics Cloud, Power BI, Excel, etc.
- Enables financial dashboards, budget vs actuals, cash flow reports
Use Cases for FDWF in Financial Reporting
Here’s how FDWF is used in real-world finance operations:
1. Group Consolidated Financial Statements
Consolidate actuals from multiple subsidiaries, adjust intercompany eliminations, and generate IFRS or GAAP-compliant reports.
2. Profit Center and Segment Reporting
Report profitability across multiple dimensions like geography, product line, or business unit.
3. Cash Flow Analysis
Track cash inflows and outflows by category and visualize funding gaps or surpluses.
4. Trial Balance Drilldown
Drill into ledger-level entries across GL accounts, company codes, and time periods.
5. Periodic and Year-End Reporting
Generate reports for month-end, quarter-end, and year-end financial closes with audit trails.
Benefits of Using FDWF
Here’s what finance teams gain from implementing FDWF:
- Consistency in data and logic across entities
- Faster month-end closing and fewer manual reconciliations
- Standardized reporting KPIs across business units
- Single source of truth for all financial reporting needs
- Data governance with audit trails and role-based access
- Scalability as your company grows or acquires new units
How to Get Started with FDWF
If your organization is already using SAP or another ERP system, here’s how you can start leveraging FDWF:
Step 1: Assess Your Current Financial Data Flow
- Identify your source systems: SAP S/4HANA, ECC, third-party tools
- Map out your reporting pain points and data quality issues
Step 2: Define Reporting Requirements
- What KPIs and metrics do you need?
- Which reports are critical for compliance or board meetings?
- What dimensions (e.g., time, entity, cost center) are required?
Step 3: Set Up the FDWF Layers
- Configure data extraction jobs
- Map and harmonize accounts, currencies, and periods
- Build VDMs for Trial Balance, P&L, Balance Sheet, etc.
Step 4: Connect to Reporting Tools
- Use SAP Analytics Cloud or Power BI to visualize reports
- Build dashboards with filters, slicers, and drilldowns
- Set up scheduled reports for stakeholders
Best Practices for FDWF Reporting
Involve business users early – Don’t build in isolation
Ensure role-based security – Only authorized users should access sensitive reports
Automate reconciliation – Use validation logic to check totals and consistency
Document your data model – Keep data dictionaries for transparency
Keep it scalable – Design with future acquisitions or mergers in mind
FDWF vs Traditional Reporting
| Feature | FDWF | Traditional Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Data Consolidation | Built-in | Manual or external tools |
| Real-Time Reporting | Supported | Limited |
| Scalability | High | Medium |
| Governance | Strong (Audit-Ready) | Often lacks audit trail |
| Multiple Source Systems | Easily Integrated | Needs custom ETL solutions |
| Reporting Flexibility | Very High | Often static and rigid |
Challenges to Watch For
Initial setup complexity – FDWF requires planning and expert setup
Data quality – Poor source data can break your reports
Change management – Finance teams need to be trained on new tools and dashboards
Licensing & infrastructure – FDWF may require additional SAP components
Final Thoughts
FDWF is not just another acronym—it’s a game-changer for financial reporting. By unifying, validating, and structuring your data, it empowers finance teams to move beyond Excel sheets and static reports to truly dynamic, real-time financial insights.
Whether you’re preparing board-level financial statements, drilling into profit margins, or managing compliance reporting, FDWF provides the foundation you need to deliver fast, accurate, and consistent financial data.
If your organization deals with multiple data sources and complex financial structures, it’s time to consider FDWF as the backbone of your reporting strategy.