The Evolution of SAP: From R/1 to SAP S/4HANA
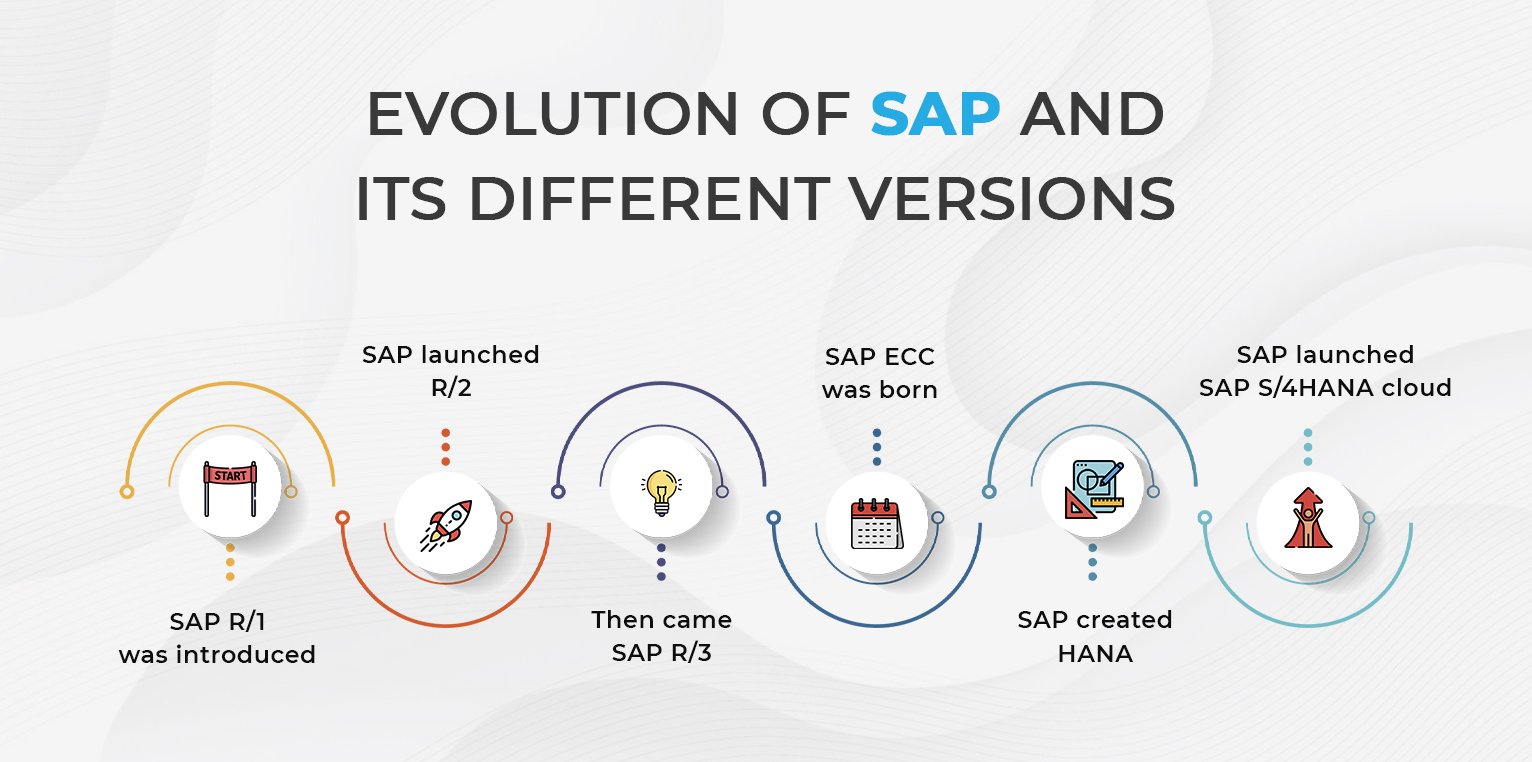
For over five decades, SAP has been at the forefront of enterprise software, shaping how businesses manage operations, finances, and customer relationships. From its early days of mainframe-based systems to today’s intelligent cloud ERP, SAP has evolved continuously to meet the changing needs of global businesses.
In this post, we’ll take a journey through the evolution of SAP ERP systems—from SAP R/1 to SAP S/4HANA—highlighting key milestones, innovations, and the future of enterprise technology.
A Brief Introduction to SAP
Founded in 1972 in Walldorf, Germany, SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) started as a small software company focused on building standard business solutions.
Today, SAP serves over 400,000 customers in 180+ countries, making it one of the largest software vendors in the world.
The Evolution of SAP ERP Systems
1. SAP R/1 (1972) – The Beginning
- SAP’s first ERP system: Real-Time Data Processing System R/1
- Architecture: Single-tier (all layers on one machine)
- Focused on financial accounting and payroll
R/1 was revolutionary in allowing real-time data processing at a time when batch processing was the norm.
2. SAP R/2 (1979) – Mainframe Era
- Introduced two-tier architecture (presentation layer + database & application layer)
- Supported multi-currency and multi-language features
- Targeted large enterprises using IBM mainframes
R/2 brought integrated business processes for manufacturing, sales, and finance, becoming the backbone of many European corporations.
3. SAP R/3 (1992) – Client-Server Revolution
- Shifted to three-tier architecture (Presentation ➔ Application ➔ Database)
- Introduced a graphical user interface (SAP GUI)
- Supported Windows, Unix, and Linux servers
R/3 made ERP more accessible and scalable for businesses beyond the mainframe world. It became the global standard for enterprise resource planning.
4. SAP ERP (ECC 5.0 & ECC 6.0) (2004–2006) – Enhanced Integration
- Evolved into SAP ERP Central Component (ECC)
- Modular design covering FI, CO, SD, MM, PP, HR, etc.
- Supported Unicode, NetWeaver platform, and enterprise services
ECC was more flexible and could be extended with industry-specific solutions. It remained dominant for over a decade.
5. SAP HANA (2011) – The In-Memory Breakthrough
- SAP launched SAP HANA (High-Performance Analytic Appliance), an in-memory database
- Enabled real-time data processing, eliminating the need for batch jobs
- Initially used for analytics and reporting, later became the foundation for ERP systems
HANA dramatically increased speed and simplified IT landscapes.
6. SAP S/4HANA (2015) – The Digital Core
- Launched as SAP’s next-generation ERP for the digital age
- Built natively on SAP HANA in-memory database
- Features:
- Universal Journal (ACDOCA)
- Fiori user experience (UX)
- Real-time insights and predictive analytics
- Simplified data model and processes
SAP S/4HANA is available both on-premise and in the cloud, helping organizations modernize their business models and adopt intelligent technologies like AI, Machine Learning, and RPA.
Key Innovations Across the SAP Journey
| SAP Version | Key Innovations | Era |
|---|---|---|
| SAP R/1 | Real-time financial processing | 1970s |
| SAP R/2 | Mainframe integration, multi-currency | 1980s |
| SAP R/3 | Client-server, GUI, modular ERP | 1990s |
| SAP ECC | NetWeaver, Unicode, industry solutions | 2000s |
| SAP HANA | In-memory computing, real-time analytics | 2010s |
| SAP S/4HANA | Cloud-native, AI/ML, simplified UX and architecture | 2015–Present |
SAP Cloud ERP: The Future
With the rise of cloud computing, SAP now offers:
- SAP S/4HANA Cloud (Public & Private editions)
- SAP Business ByDesign (for mid-sized companies)
- SAP Business One (for small businesses)
Additionally, RISE with SAP helps businesses transform to cloud ERP with bundled services, infrastructure, and business process intelligence.
Why Businesses Upgrade to SAP S/4HANA
- Real-time business insights
- Simplified IT landscapes
- Improved user experience (SAP Fiori)
- Embedded AI and analytics
- Enhanced regulatory compliance
- Scalability for global operations
With the 2027 deadline for SAP ECC maintenance, many organizations are already moving toward S/4HANA to stay future-ready.
SAP Beyond ERP: The Intelligent Enterprise
SAP is no longer just an ERP vendor. Its vision is to power the Intelligent Enterprise through:
- SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP)
- SAP Ariba, SuccessFactors, Concur, Fieldglass (Cloud Line of Business solutions)
- SAP Analytics Cloud
- SAP AI & Machine Learning
By integrating data, processes, and experience management (with Qualtrics), SAP is helping businesses run smarter, faster, and more sustainably.
Conclusion
From SAP R/1 to SAP S/4HANA, the journey of SAP reflects not just the evolution of technology but the transformation of how businesses operate in a digital world.
SAP continues to innovate—empowering organizations of all sizes to simplify processes, drive agility, and deliver value in an ever-changing market.
As we look ahead, the shift to cloud ERP and intelligent technologies will define the next chapter in the SAP story.